Describe How Utility Is Used in Cost Benefit Analysis
Currently the best economic evaluation method for doing this is cost-utility analysis. Cost-benefit analysis is defined as an approach to determine the weaknesses and strengths of action in business.

Cost Benefit Analysis And The Environment Further Developments And Policy Use En Oecd
Discuss outcomes in cost-effectiveness analysis and cost.

. While cost-benefit analysis asks whether the economic benefits outweigh the economic costs of a given policy cost-effectiveness analysis is focused on the question of how much it costs to get a certain amount of output from a policy. A form of cost-effectiveness analysis that presents costs and outcomes in discrete categories without aggregating or weighting them. Several techniques are available with the most common being the payback period net present value and rate of return.
This report Cost-Benefi t Analysis and the Environment. This book provides a more comprehensive explanation of the methods used in cost benefit analysis including the different approaches for valuing effects in. These techniques essentially compare the total capital investment for the project against its potential returns.
Discuss what cost-effectiveness analysis Is and when the analysis is appropriate. There has been uncertainty in the conduct of such economic evaluations in India due to some hesitancy with respect to the adoption of their guidelines. Cost-benefit analysis is a way to compare the costs and benefits of an intervention where both are expressed in monetary units.
For instance in simplistic terms cost-effectiveness analysis assesses the cost of gaining health outcomes eg life-years gained between alternative programs. A standard test applied to a process to determine if the net present value of costs associated with an activity will exceed a benchmark or other limit. The first is an examination of the use of utility as an object of measurement.
Outcomes are measured in units of morbidity-adjusted survival called the quality-adjusted life year QALY. Requires a common outcome measure. Learning Objectives Discuss what cost-benefit analysts is and when the analysis Is appropriate.
Three cost analyses with greatest utility to states and districts are cost-effectiveness cost -feasibility and cost-benefit. A form of cost-effectiveness analysis that compares costs in monetary units with outcomes in terms of their utility usually to the patient measured eg in QALYs Cost-consequence analysis. It is argued that as it is often conceived and measured utility is not an appropriate unit.
Further Developments and Policy Use provides a timely update on recent developments in the theory and practice of cost-benefi t analysis. The traditional classification of economic evaluation includes cost-minimization cost-effectiveness analysis cost-utility analysis and cost-benefit analysis. Cost-feasibility analysis compares total cost to available.
Cost tests are often paired with. To clearly compile a comprehensive list of costs as a best practice consider the external and internal costs of the project. However CBA places a monetary value on health outcomes so that both costs and benefits are in monetary units such as dollars.
This method it is not often used in health care studies. Yet there are ethical limits to the use of some economic arguments frequently made in opposition to proposed government action to reduce greenhouse gas emissionsCost-benefit analysis CBA of some environmental regulatory programs can help identify proposed market regulatory interventions whose costs significantly outweigh environmental benefits. Cost-utility analysis considers individuals or societies preference related to a health outcome eg quality-adjusted life-years QALYs.
Cost-benefit Benefits - Costs AKA net benefits OR. Cost utility analysis CUA is an economic analysis in which the incremental cost of a program from a particular point of view is compared to the incremental health improvement expressed in the unit of quality adjusted life years QALYs 6. This compares the costs of different procedures with their outcomes measured in utility based units--that is units that relate to a persons level of wellbeing.
A Cost-Benefit Analysis expresses outcomes in dollars rather than QALYs. Cost benefit analysis can be used to evaluate a single path or to compare multiple paths. Cost-effectiveness analysis compares the ratio of a unit increase in outcome to cost.
The most commonly used unit is the quality adjusted life year QALY. Cost-utility analysis CUA. Once the scope is defined costs should be identified and categorized.
Cost-benefit analysis techniques are a common business activity owners and managers use to assess various projects. 49 rows For example cost utility analysis may be used in health care to decide. A Cost-Utility Analysis examines the incremental effect of health care interventions on both cost and outcomes.
The cost-benefit analysis determines the best course of action to achieve benefits. Both CBA and cost-effectiveness analysis CEA include health outcomes. A persons utility takes into account the monetary and nonmonetary costs and benefits of a decision so a person using cost-benefit analysis is figuring his or her utility for different outcomes Describe the difference between monetary and nonmonetary considerations.
Formulas to calculate the two are listed below. Describe how utility is used in cost-benefit analysis. 2006 OECD publication Cost-Benefi t Analysis and the Environment.
There are two main themes. Cost-benefit analysis translates health outcomes such as life-years gained. CUA is used to determine cost in terms of utilities to say in quantity and quality of life.
The number of services used. When theres just one path in question the tool can suggest whether to pursue that path or stay put. Discuss limitations of cost-benefit analysis.
Describe willingness to pay as an outcome measure in cost-benefit analysis. This paper re-examines the question of the appropriate unit of measurement in cost utility analysis and the technique that will measure it. It is a decision making concept employed to understand the cost of a given transaction by comparing it with the derived benefits.
Thus net benefits can be positive ie drug court participants used fewer resources overall than the comparison group of those on probation or negative where the total end result. When there are multiple paths the tool can help to identify the best choice by looking at the benefit-cost ratio of each option. As with cost utility analysis.
Recent Developments has been a reference publication for more than a decade. Although cost-benefit analysts use the term frequently net benefit can be slightly misleading it is the difference between total costs and total benefits. Total utility explicit costs implicit costs.

Economic Evaluation Types Of Economic Evaluation Public Health Notes

Cost Benefit Analysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
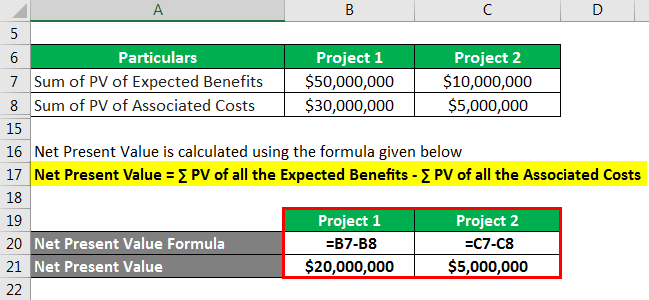
Cost Benefit Analysis Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template
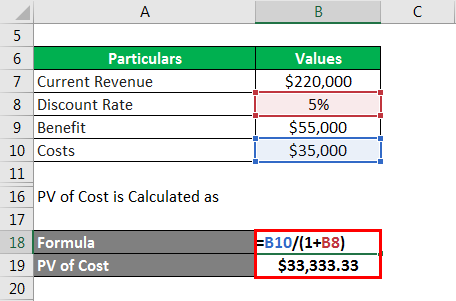
Cost Benefit Analysis Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template

What Is Cost Benefit Analysis Definition Examples Faqs
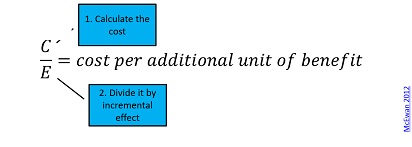
Cost Effectiveness Analysis Dime Wiki

What Is Cost Benefit And Cost Effectiveness Analysis By Prof Katherine Payne Youtube
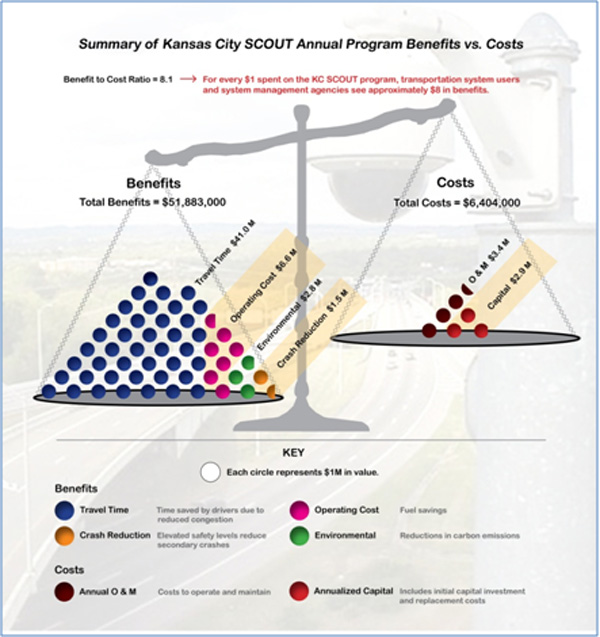
Operations Benefit Cost Analysis Desk Reference Chapter 2 Overview Of B C Analysis For Operations
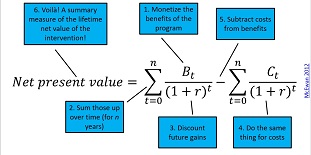
Cost Effectiveness Analysis Dime Wiki
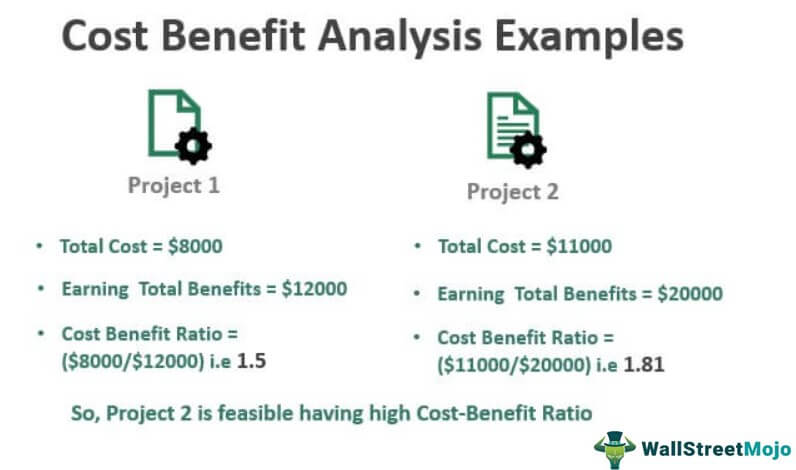
Cost Benefit Analysis Examples Top 3 Cba Examples With Explanation
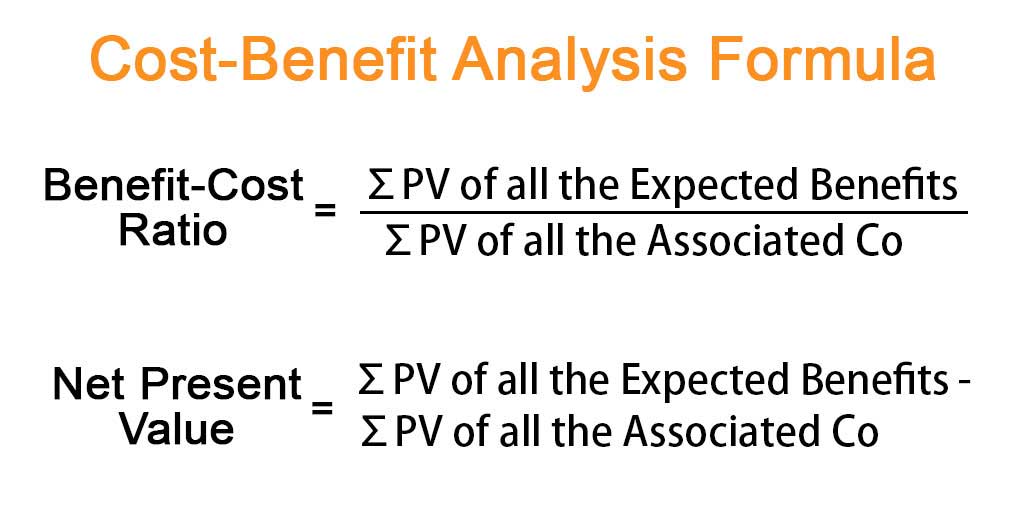
Cost Benefit Analysis Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template
What Is Cost Benefit And Cost Effectiveness Analysis By Prof Katherine Payne Youtube

Cost Benefit Analysis Example Analysis Business Analysis Inspirational Quotes Motivation
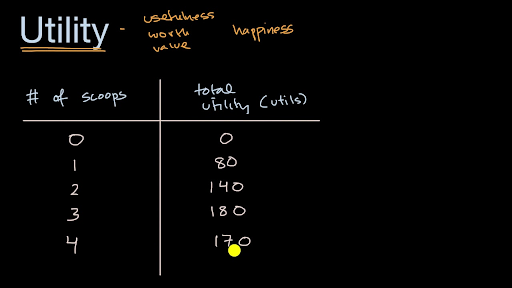
Introduction To Utility Video Khan Academy

Difference Between Cost Effectiveness Analysis And Cost Benefit Analysis Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



Comments
Post a Comment